

The sets of reserved and unreserved characters and the circumstances under which certain reserved characters have special meaning have changed slightly with each revision of specifications that govern URIs and URI schemes. Using percent-encoding, reserved characters are represented using special character sequences. Unreserved characters have no such meanings. For example, forward slash characters are used to separate different parts of a URL.
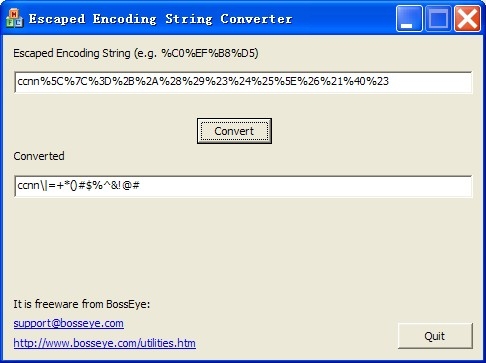
Reserved characters are those characters that sometimes have special meaning. The characters allowed in a URI are either reserved or unreserved. As such, it is also used in the preparation of data of the application/x-www-form-urlencoded media type, as is often used in the submission of HTML form data in HTTP requests. Although it is known as URL encoding it is, in fact, used more generally within the main Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) set, which includes both Uniform Resource Locator (URL) and Uniform Resource Name (URN). Percent-encoding, also known as URL encoding, is a mechanism for encoding information in a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) under certain circumstances. The online decoder tool takes the encoded URL as input and outputs the decoded URL. This is done to ensure that the URL is properly formatted and can be transmitted over the internet. The URL encoding process replaces certain characters in a URL with their corresponding ASCII code. Our online URL decoder tool helps you to convert an encoded URL into a readable format.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
